Fish Redux中的Dispatch是怎么实现的?
开源地址:https://github.com/alibaba/fish-redux
我们在使用fish-redux构建应用的时候,界面代码(view)和事件的处理逻辑(reducer,effect)是完全解耦的,界面需要处理事件的时候将action分发给对应的事件处理逻辑去进行处理,而这个分发的过程就是下面要讲的dispatch, 通过本篇的内容,你可以更深刻的理解一个action是如何一步步去进行分发的。
从example开始为了更好的理解action的dispatch过程,我们就先以todolistpage中一条todo条目的勾选事件为例,来看点击后事件的传递过程,通过断点debug我们很容易就能够发现点击时候发生的一切,具体过程如下:
用户点击勾选框,GestureDetector的onTap会被回调
通过buildView传入的dispatch函数对doneAction进行分发,发现todo_component的effect中无法处理此doneAction,所以将其交给pageStore的dispatch继续进行分发
pageStore的dispatch会将action交给reducer进行处理,故doneAction对应的_markDone会被执行,对state进行clone,并修改clone后的state的状态,然后将这个全新的state返回
然后pageStore的dispatch会通知所有的listeners,其中负责界面重绘的_viewUpdater发现state发生变化,通知界面进行重绘更新
Dispatch实现分析Dispatch在fish-redux中的定义如下
typedef Dispatch = void Function(Action action);本质上就是一个action的处理函数,接受一个action,然后对action进行分发。
下面我门通过源码来进行详细的分析。
01 component中的dispatch
buildView函数传入的dispatch是对应的component的mainCtx中的dispatch, _mainCtx和componet的关系如下 component->ComponentWidget->ComponentState->_mainCtx->_dispatch而 _mainCtx的初始化则是通过componet的createContext方法来创建的,顺着方法下去我们看到了dispatch的初始化
// redux_component/context.dart DefaultContext初始化方法
DefaultContext({
@requiredthis.factors,
@requiredthis.store,
@requiredBuildContext buildContext,
@requiredthis.getState,
}):assert(factors !=null),
assert(store !=null),
assert(buildContext !=null),
assert(getState !=null),
_buildContext = buildContext {
finalOnAction onAction = factors.createHandlerOnAction(this);
/// create Dispatch
_dispatch = factors.createDispatch(onAction,this, store.dispatch);
/// Register inter-component broadcast
_onBroadcast =
factors.createHandlerOnBroadcast(onAction,this, store.dispatch);
registerOnDisposed(store.registerReceiver(_onBroadcast));
}
context中的dispatch是通过factors来进行创建的,factors其实就是当前component,factors创建dispatch的时候传入了onAction函数,以及context自己和store的dispatch。onAction主要是进行Effect处理。这边还可以看到,进行context初始化的最后,还将自己的onAction包装注册到store的广播中去,这样就可以接收到别人发出的action广播。
Component继承自Logic
// redux_component/logic.dart
@override
Dispatch createDispatch(
OnAction onAction,Context<T> ctx,Dispatch parentDispatch){
Dispatch dispatch =(Action action){
throwException(
Dispatching while appending your effect & onError to dispatch is not allowed.);
};
/// attach to store.dispatch
dispatch = _applyOnAction<T>(onAction, ctx)(
dispatch:(Action action)=> dispatch(action),
getState:()=> ctx.state,
)(parentDispatch);
return dispatch;
}
staticMiddleware<T> _applyOnAction<T>(OnAction onAction,Context<T> ctx){
return({Dispatch dispatch,Get<T> getState}){
return(Dispatchnext){
return(Action action){
finalObject result = onAction?.call(action);
if(result !=null&& result !=false){
return;
}
//skip-lifecycle-actions
if(action.type isLifecycle){
return;
}
if(!shouldBeInterruptedBeforeReducer(action)){
ctx.pageBroadcast(action);
}
next(action);
};
};
};
}
}

上面分发的逻辑大概可以通过上图来表示
通过onAction将action交给component对应的effect进行处理
当effect无法处理此action,且此action非lifecycle-actions,且不需中断则广播给当前Page的其余所有effects
最后就是继续将action分发给store的dispatch(parentDispatch传入的其实就是store.dispatch)
02 store中的dispatch
从store的创建代码我们可以看到store的dispatch的具体逻辑
// redux/create_store.dart
finalDispatch dispatch =(Action action){
_throwIfNot(action !=null,Expected the action to be non-null value.);
_throwIfNot(
action.type !=null,Expected the action.type to be non-null value.);
_throwIfNot(!isDispatching,Reducers may not dispatch actions.);
try{
isDispatching =true;
state = reducer(state, action);
}finally{
isDispatching =false;
}
finalList<_VoidCallback> _notifyListeners = listeners.toList(
growable:false,
);
for(_VoidCallback listener in _notifyListeners){
listener();
}
notifyController.add(state);
};
store的dispatch过程比较简单,主要就是进行reducer的调用,处理完成后通知监听者。
03 middleware
Page继承自Component,增加了middleware机制,fish-redux的redux部分本身其实就对middleware做了支持,可以通过StoreEnhancer的方式将middlewares进行组装,合并到Store的dispatch函数中。
middleware机制可以允许我们通过中间件的方式对redux的state做AOP处理,比如fish-redux自带的logMiddleware,可以对state的变化进行log,分别打印出state变化前和变化后的值。
当Page配置了middleware之后,在创建pageStore的过程中会将配置的middleware传入,传入之后会对store的dispath进行增强加工,将middleware的处理函数串联到dispatch中。
// redux_component/component.dart
Widget buildPage(P param){
return wrapper(_PageWidget<T>(
component:this,
storeBuilder:()=> createPageStore<T>(
initState(param),
reducer,
applyMiddleware<T>(buildMiddleware(middleware)),
),
));
}
// redux_component/page_store.dart
PageStore<T> createPageStore<T>(T preloadedState,Reducer<T> reducer,
[StoreEnhancer<T> enhancer])=>
_PageStore<T>(createStore(preloadedState, reducer, enhancer));
// redux/create_store.dart
Store<T> createStore<T>(T preloadedState,Reducer<T> reducer,
[StoreEnhancer<T> enhancer])=>
enhancer !=null
? enhancer(_createStore)(preloadedState, reducer)
: _createStore(preloadedState, reducer);
所以这里可以看到,当传入enhancer时,createStore的工作被enhancer代理了,会返回一个经过enhancer处理过的store。而PageStore创建的时候传入的是中间件的enhancer。
// redux/apply_middleware.dart
StoreEnhancer<T> applyMiddleware<T>(List<Middleware<T>> middleware){
return middleware ==null|| middleware.isEmpty
?null
:(StoreCreator<T> creator)=>(T initState,Reducer<T> reducer){
assert(middleware !=null&& middleware.isNotEmpty);
finalStore<T> store = creator(initState, reducer);
finalDispatch initialValue = store.dispatch;
store.dispatch =(Action action){
throwException(
Dispatching while constructing your middleware is not allowed.
Other middleware would not be applied to this dispatch.);
};
store.dispatch = middleware
.map((Middleware<T> middleware)=> middleware(
dispatch:(Action action)=> store.dispatch(action),
getState: store.getState,
))
.fold(
initialValue,
(Dispatch previousValue,
DispatchFunction(Dispatch) element)=>
element(previousValue),
);
return store;
};
}
这里的逻辑其实就是将所有的middleware的处理函数都串到store的dispatch,这样当store进行dispatch的时候所有的中间件的处理函数也会被调用。下面为各个处理函数的执行顺序,
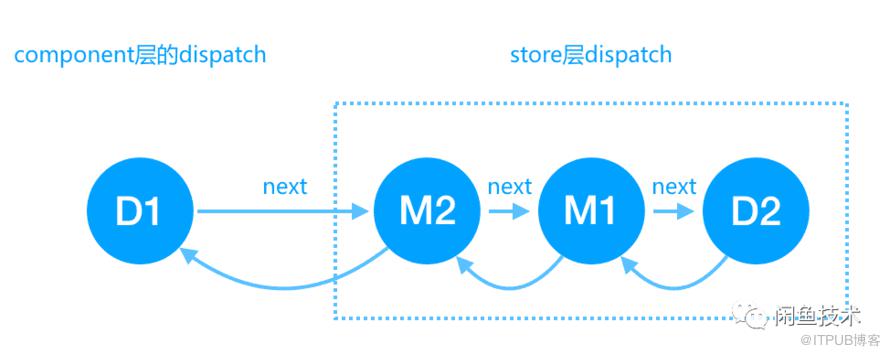
首先还是component中的dispatch D1 会被执行,然后传递给store的dispatch,而此时store的dispatch已经经过中间件的增强,所以会执行中间件的处理函数,最终store的原始dispatch函数D2会被执行。
总结通过上面的内容,现在我们可以知道一个action是如何一步步的派送给effect,reducer去进行处理的,我们也可以通过middleware的方式去跟踪state的变化,这样的扩展性给框架本身带来无限可能。
扫一扫,关注我们

